Get started with Amazon DynamoDB
Step-by-step instructions to ingest DynamoDB data to Propel.
Architecture
Amazon DynamoDB Pools in Propel consume the change data capture DynamoDB streams via Amazon Data Firehose.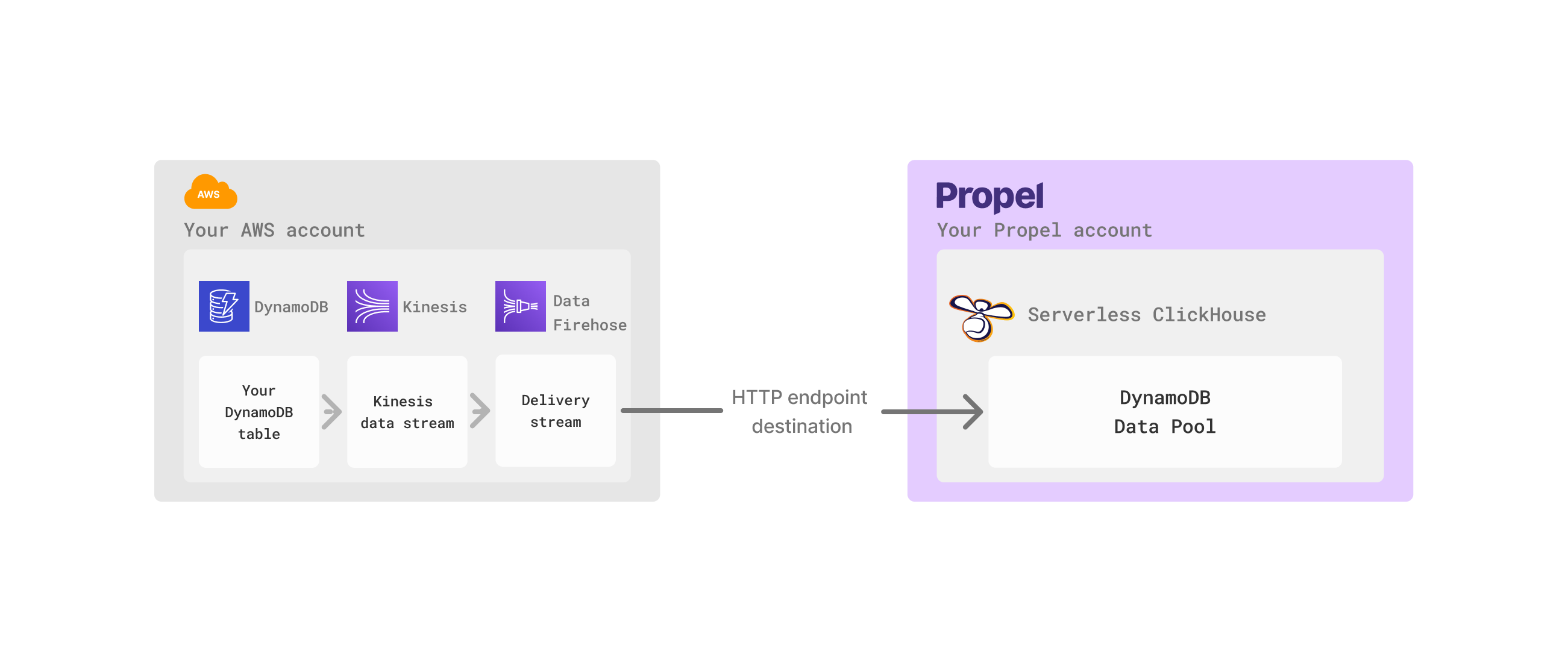
Features
Amazon DynamoDB ingestion supports the following features:| Feature name | Supported | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Event collection | ✅ | Collects change data capture events from DynamoDB streams. |
| Real-time updates | ✅ | See the Real-time updates section. |
| Real-time deletes | ✅ | See the Real-time deletes section. |
| Batch Delete API | ✅ | See Batch Delete API. |
| Batch Update API | ✅ | See Batch Update API. |
| Bulk insert | ✅ | Up to 500 events per HTTP request. |
| API configurable | ✅ | See API docs. |
| Terraform configurable | ✅ | See Terraform docs. |
How does the Amazon DynamoDB Data Pool work?
The Amazon DynamoDB Data Pool works by consuming the change data capture events DynamoDB produces to a Kinesis data stream. When your DynamoDB tables change, these events are captured by the Kinesis data stream and forwarded through Amazon Data Firehose to a secure Propel HTTP endpoint. This enables real-time data ingestion and synchronization between your DynamoDB database and Propel. Propel handles the special encoding, data format, and basic authentication required for receiving events via Amazon Data Firehose. By default, the Amazon DynamoDB Data Pool have the following columns:| Column | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
_propel_received_at | TIMESTAMP | The timestamp when the event was collected in UTC. |
_propel_payload | JSON | The JSON payload of the event. |
event_id | STRING | The event unique ID. |
event_name | STRING | The event name: INSERT, MODIFY, or REMOVE. |
event_source | STRING | The event source: aws:dynamodb. |
record_format | STRING | The record format: JSON. |
user_identity | JSON | The user identity. |
aws_region | STRING | The AWS region. |
approximate_creation_date_time | INT64 | The approximate event creation date time. |
approximate_creation_date_time_precision | STRING | The timestamp precision. |
keys | JSON | The DynamoDB partition and sorting key values. |
new_image | JSON | The new JSON object. |
old_image | JSON | The old JSON object. |
size_bytes | INT64 | The size bytes. |
When creating an Amazon DynamoDB Data Pool, you can flatten top-level or nested JSON keys into specific columns.
Schema changes
The Amazon DynamoDB Data Pool is designed to handle semi-structured, schema-less JSON data. This flexibility allows you to add new properties to your payload as needed. The entire payload is always stored in the_propel_payload column.
However, Propel enforces the schema for required fields. If you stop providing data for a required field that was previously unpacked into its own column, Propel will return an error.
Adding Columns
1
Go to the Schema tab
Go to the Data Pool and click the “Schema” tab. Click the “Add Column” button to define the new column.
Click the “Add Column” button to define the new column.

2
Add column
Specify the JSON property to extract, the column name, and the type and click “Add column”.

3
Track progress
After clicking adding the column, an asynchronous operation will begin to add the column to the Data Pool. You can track the progress in the “Operations” tab.

Note that adding a column does not backfill existing rows. To backfill, run a batch update operation.
Column deletions, modifications, and data type changes are not supported as they are breaking changes to the schema. If you need to change the schema, you can create a new Data Pool.
Data Types
The table below shows the default mappings from JSON types to Propel types. You can change these mappings when creating an Amazon Data Firehose Data Pool.| JSON Type | Propel Type |
|---|---|
| String | STRING |
| Number | DOUBLE |
| Object | JSON |
| Array | JSON |
| Boolean | BOOLEAN |
| Null | JSON |
Limits
- Each POST request can include up to 500 events (as a JSON array).
- The payload size can be up to 1 MiB.
Best Practices
- Maximize the number of events per request, up to 500 events or 1 MiB, to enhance ingestion speed.
- Implement exponential backoff for retries on 429 (Too Many Requests) and 500 (Internal Server Error) responses to prevent data loss.
- Set up alerts or notifications for 413 (Content Too Large) errors, as these indicate exceeded event count or payload size, and retries will not resolve the issue.
- Ensure the Amazon Data Firehose Data Pool is created with all necessary fields. Utilize a sample event and the “Extract top-level fields” feature during setup.
- Assign the correct event timestamp as the default. If your event lacks a timestamp, use the
_propel_received_atcolumn. - Configure all fields, except the default timestamp, as optional to minimize 400 (Bad Request) errors. This configuration allows Propel to process requests even with missing data, which can be backfilled later.
- Set up alerts or notifications for 400 errors, as these signify schema issues that require attention, and retries will not resolve them.
- Confirm that all data types are correct. Objects, arrays, and dictionaries should be designated as JSON in Propel.
Transforming data
Once your data is in a DynamoDB Data Pool, you can use Materialized Views to:- Flatten nested JSON into tabular form
- Flatten JSON array into individual rows
- Combine data from multiple source Data Pools through JOINs
- Calculate new derived columns from existing data
- Perform incremental aggregations
- Sort rows with a different sorting key
- Filter out unnecessary data based on conditions
- De-duplicate rows
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take for an event to be available via SQL or the API?
How long does it take for an event to be available via SQL or the API?
It will depend on the buffer you set and the internal buffers Propel uses to optimize performance. It can range from 10 seconds to 2 minutes depending on the buffer size.

